HBM140: The New Black Wall Street
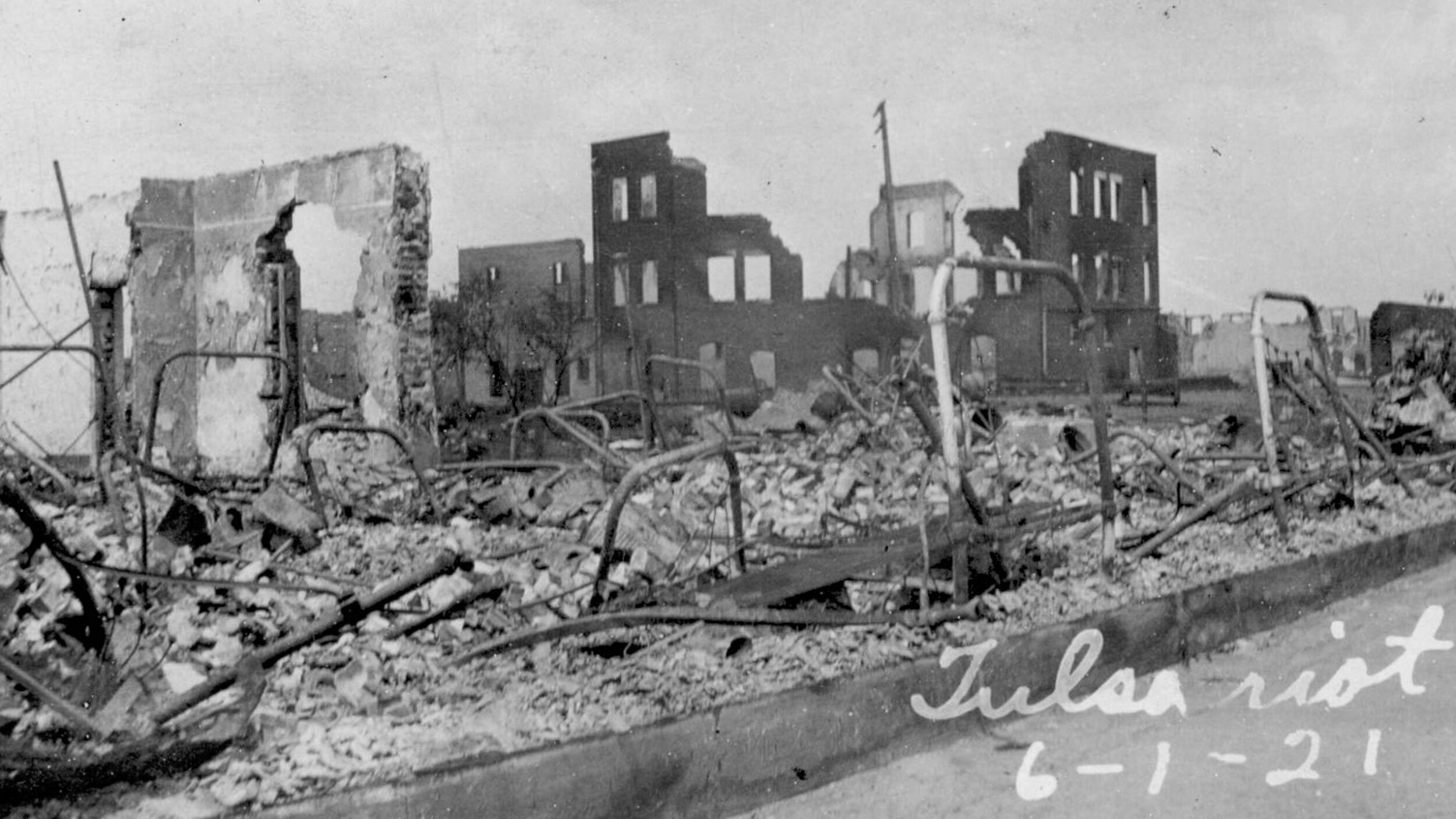
/A man surveying the damage of the Tulsa Race Massacre in 1921 with a sun rising and pillars of smoke billowing. Original image from the collection of the Oklahoma Historical Society. Digital collage by Jeff Emtman.
There used to be a neighborhood in Tulsa where Black people were wealthy. They owned businesses, built a giant church, a public library. Some Black Tulsans even owned airplanes. Booker T. Washington called it “Black Wall Street.” Others called it “Little Africa” and today, most call it “Greenwood.”
Content Note: Descriptions of racial violence, several mentions of a suicide, language.
In the early 1900s, the neighborhood was prosperous and thriving, but Black Tulsans were still a racial minority in a young city that already had a reputation for vigilante justice. A local chapter of the KKK was starting to form.
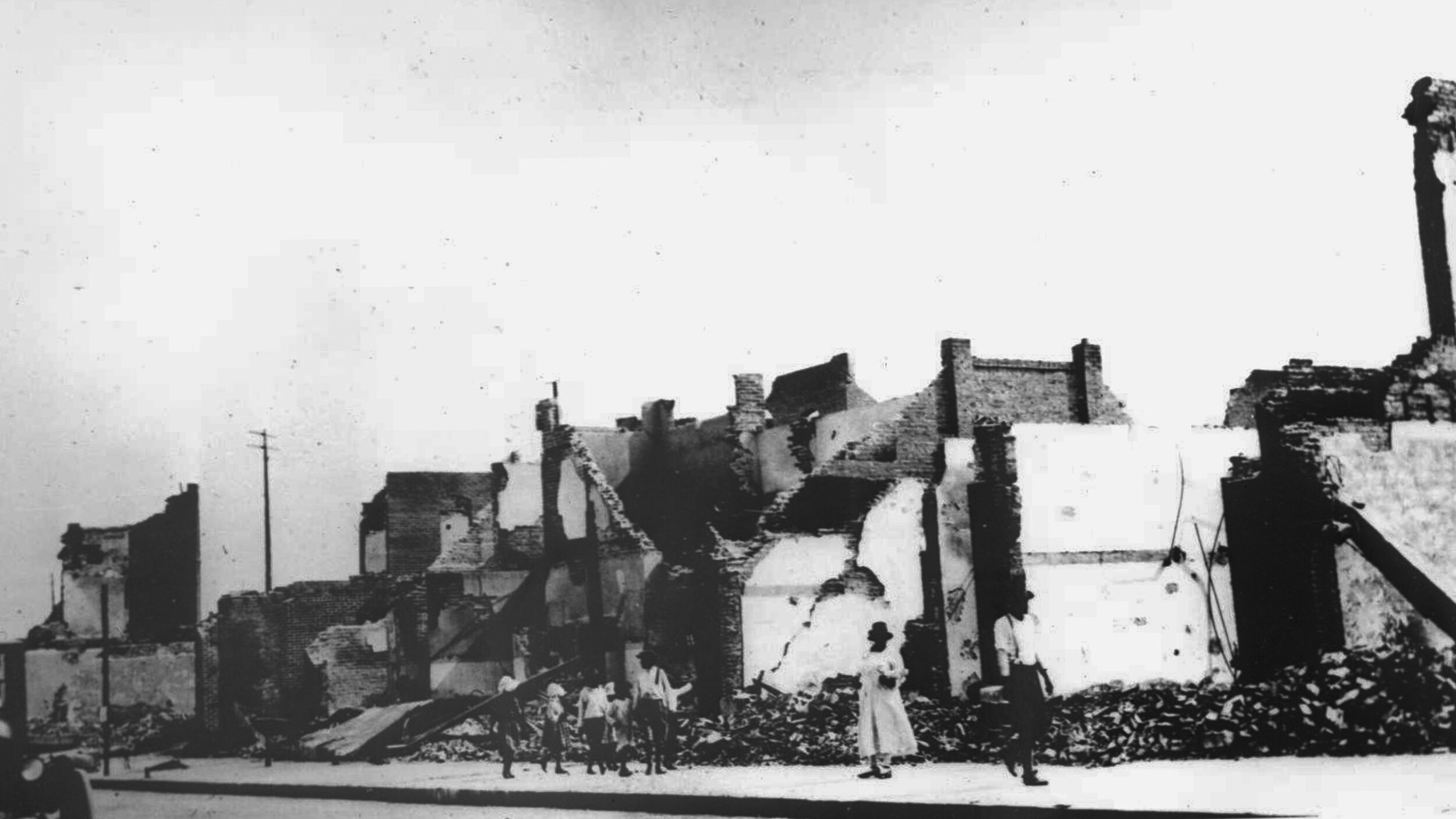
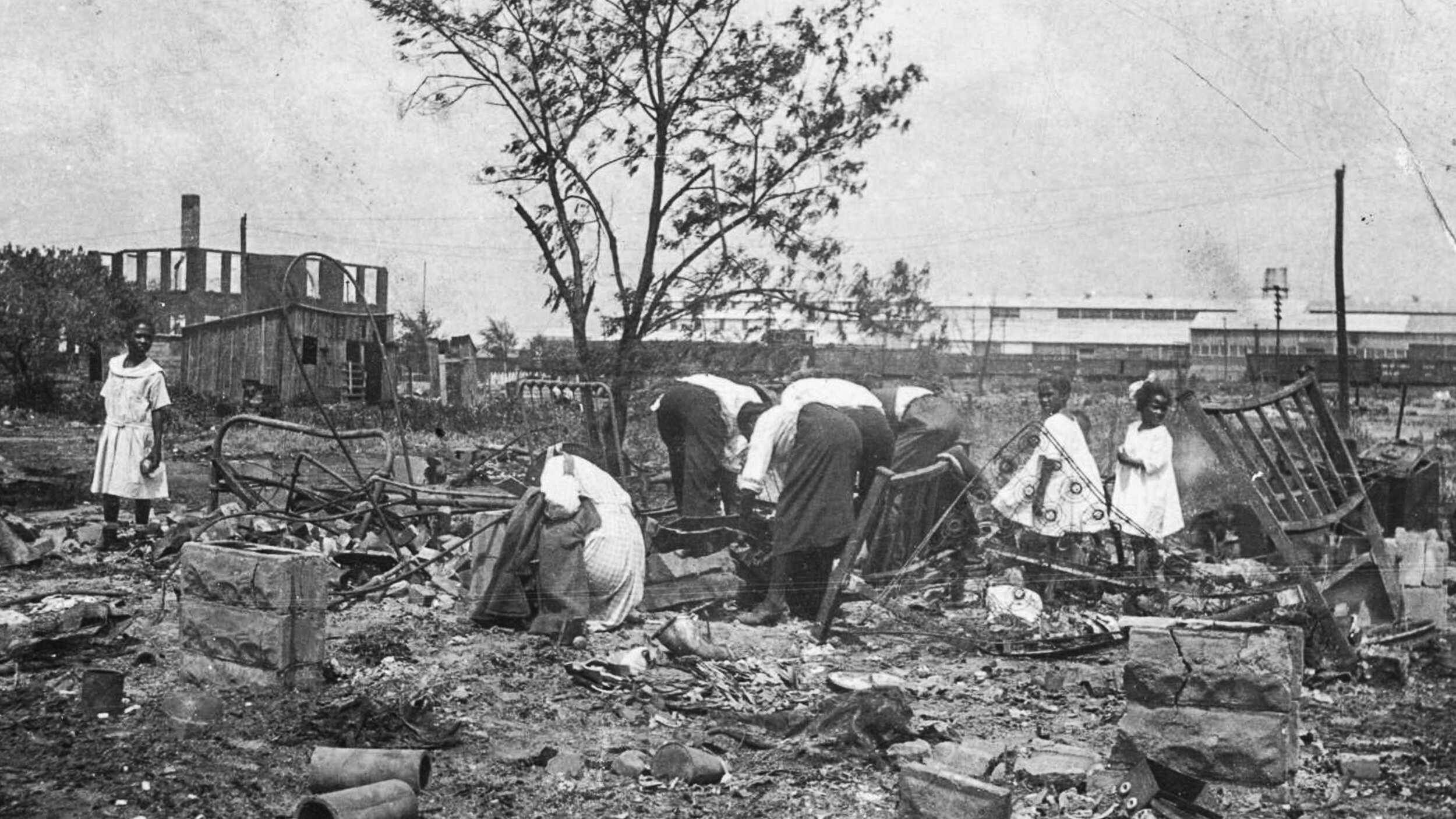
In the Spring of 1921, a Black shoe shiner named Dick Rowland was brought into custody for allegedly assaulting a white woman. Over the coming night and day, a huge mob of white Tulsans burned and looted and murdered in Greenwood and the surrounding areas. Dozens or possibly even hundreds of Black Tulsans died, thousands became homeless.
But authorities never held anyone responsible. In fact, they detained many Black residents, some for up to a week. And insurance claims made in the aftermath were denied, as the insurance policies did not cover “riots.”
In the decades that followed. Records of the event went missing, some fear they were destroyed. The mass graves have yet to be found. And many Black Tulsans believed they could face retribution for speaking out about the event. It wasn’t even taught in school until recently.
As a result, a lot of Tulsans still don’t know the history of Greenwood.
Local rapper Steph Simon was one of them. He grew up near Greenwood, and he went to middle school there. But it wasn’t until his 20’s when he stumbled upon a documentary about the massacre on Youtube. From there, he became obsessed with learning more about the true story of Tulsa. And in 2019, he released an album called Born on Black Wall Street where he reintroduces himself as “Diamond Dicky Ro” in homage to the young shoeshiner whom white mobs tried and failed to lynch on that night in 1921.
In 2011, an Oklahoman journalist named Lee Roy Chapman wrote an article for the publication This Land. Chapman’s story, The Nightmare in Dreamland, was a devastating re-telling of the life’s story of an Oklahoman legend--a “founder” of Tulsa named Tate Brady. Brady was well known as an oil tycoon and hotel owner who ran in the elite circles. However, buried by history was Brady’s legacy of violence and racial animus. He was a defender of the Confederacy, he was credibly accused of tarring and feathering some IWW union members, and for part of his life, he was in the Ku Klux Klan. And on the night of the massacre, Brady was there, acting as a night watchman. He reported seeing several dead black people in the streets in or around Greenwood.
With these revelations, a movement started to remove the Brady name from Tulsa. That movement succeeded partially, but the Brady name is still a part of the Tulsan landscape.
When Steph Simon shot the cover image for Born On Black Wall Street, he wanted to incorporate the symbolism of Tate Brady. So he went to Brady’s former mansion—a house modelled visually after the house of Robert E. Lee’s, with murals of the Confederacy painted inside and big stone columns out front. It sits on a hill overlooking historic Greenwood. And he stood on the front steps of the mansion only to see a childhood friend driving by. It was Felix Jones, an ex-NFL running back. The two grew up together. To Simon’s surprise, Jones revealed that he’d just bought the mansion. And he invited Simon inside.
Together they thought up ideas on how to transform the legacy of the house from something hateful to something loving. So Simon invited about a hundred Black kids to come have a party on the lawn while he filmed the music video for his single “Upside”.
After that, Simon and Jones started throwing concerts there, drawing huge crowds and starting the slowly re-contextualizing the house into something positive. They renamed the house “Skyline Mansion.”
As this transformation took place, another local DJ and producer, Stevie Johnson woke up in a cold sweat one night. He’d had a dream about rebuilding Black Wall Street, figuratively and literally. He opened his laptop and wrote down his ideas frantically, trying to remember his vision. And soon after, he started to act on it.
His first step was Fire in Little Africa: a commemorative rap album to mark the 100th anniversary of the Tulsa Race Massacre, featuring nearly sixty artists from Oklahoma. And over the course of a weekend in early 2020, rappers and community members and businesses filled Skyline Mansion to record dozens of tracks for the album.
Fire in Little Africa will be available in February of 2021. Their podcast is out now. They’re also curating spotify playlists of the featured artists, and they’re accepting donations via the Tulsa Community Foundation.
On this episode of Here Be Monsters, Taylor Hosking visits the former Brady Mansion to talk to the musicians who are looking to build a new Black Wall Street in Tulsa. Taylor also published an article in CityLab called Avenging the Tulsa Race Massacre With Hip Hop.
A lot of people and organizations helped make this episode possible. We’d like to thank Steph Simon, Verse, Stevie Johnson, Keeng Cut, Written Quincy, Bobby Eaton, Felix Jones, Dan Hanh, Mechelle Brown, Chris Davis, Shruti Dhalwala, Brandon Oldham, Ben Lindsey, John DeLore, The George Kaiser Family Foundation, The Oklahoma Historical Society, and The Woody Guthrie Center.
Producer: Taylor Hosking (Instagram) (Twitter)
Editor: Jeff Emtman
Music: Steph Simon, Verse, (see embedded YouTube playlist 😀☝) The Black Spot
Also heard on this episode: recordings from Black Lives Matter protests made by Neroli Price of Seattle, Washington; Bryanna Buie of Wilmington, North Carolina; and Bethany Donkin of Oxford, UK.
More About the Tulsa Race Massacre:
- Official Report from 2001 which describes the events of 1921 in detail and with context.
- Educational comic about the massacre published by the Atlantic and sponsored by HBO’s Watchmen.
- Riot and Remembrance By James S. Hirsch